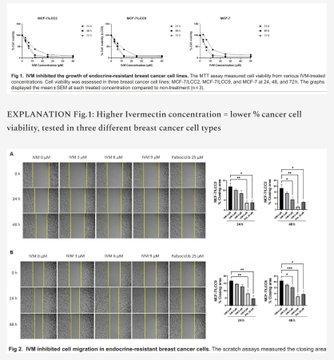
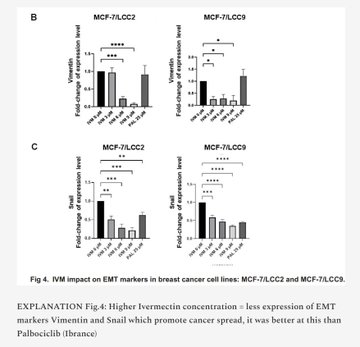
新文章:伊维菌素——伊维菌素如何抑制乳腺癌扩散?2025年泰国论文,作者:Rujimongkon等人。亮点:本文探讨了伊维菌素是否可以“重新利用”,作为对抗某些难治性乳腺癌的潜在辅助药物。研究人员在实验室培养的乳腺癌细胞上测试了伊维菌素,特别是那些不再对激素疗法(如他莫昔芬或氟维司群)产生反应的细胞类型。主要发现:伊维菌素能减缓癌细胞的生长:它能阻止这些耐药癌细胞快速增殖。有效剂量处于合理范围内(微摩尔级,与其他实验室研究结果相似),且对耐药细胞和普通乳腺癌细胞的疗效相当。正常(非癌变)乳腺细胞受到的影响较小,表明该药物对癌细胞具有选择性。它或许有助于克服耐药性:当与他莫昔芬(一种标准激素疗法)联合使用时,较低剂量的他莫昔芬仍然有效,这表明伊维菌素可能使耐药性癌症再次变得敏感。它能降低癌症扩散的可能性:当癌细胞变得更具移动性和侵袭性时,癌症就会扩散(转移)。实验室测试表明,伊维菌素能够抑制癌细胞的迁移和侵袭能力。它部分是通过逆转“上皮-间质转化”(EMT)来实现这一目标的——EMT 是一种癌细胞变得更具侵袭性和更容易扩散的过程。具体来说,伊维菌素降低了波形蛋白和蜗牛蛋白(促进扩散)等蛋白质的水平,并可能有助于恢复 E-钙黏蛋白(使细胞粘在一起)。本文重点研究了 Wnt 信号通路,该通路在乳腺癌中经常过度活跃,并驱动癌细胞的生长和扩散。伊维菌素减少了某些 Wnt“信号”(如 Wnt5a/b 配体)和一种受体(LRP6),从而减少了 EMT,并可能减缓了疾病进展。在耐药细胞中,这种效应更为显著。研究人员将伊维菌素与一种用于治疗类似耐药性乳腺癌的已批准药物帕博西尼(Ibrance)进行了比较,发现伊维菌素在阻止某些与扩散相关的变化方面更有效。结论:这些实验室结果表明,伊维菌素对激素治疗耐药的乳腺癌细胞具有良好的抗生长和抗扩散作用,可能是通过干扰 Wnt 通路和 EMT 实现的。我的看法……我经常被问到——伊维菌素是一种抗寄生虫药物,它怎么可能治疗癌症呢?答案是:伊维菌素的作用远不止是抗寄生虫药。伊维菌素具有广泛的抗肿瘤特性!ARTICLE: IVERMECTIN - How does Ivermectin inhibit spread of Breast Cancer? 2025 Thailand paper by Rujimongkon et al.HIGHLIGHTS:This paper explores whether Ivermectin could be “repurposed” as a potential helper in fighting certain tough-to-treat breast cancers.Researchers tested Ivermectin on lab-grown breast cancer cells, specifically types that no longer respond to hormone therapies (like tamoxifen or fulvestrant). KEY FINDINGS:Ivermectin slows cancer cell growth: It stops these resistant cancer cells from multiplying as quickly. The effective doses were in a realistic range (micromolar levels, similar to what’s seen in other lab studies), and it worked about as well on resistant cells as on regular breast cancer cells. Normal (non-cancer) breast cells were less affected, suggesting selectivity for cancer cells.It may help overcome drug resistance: When combined with tamoxifen (a standard hormone therapy), lower doses of tamoxifen still worked, hinting that Ivermectin could make resistant cancers sensitive again.It reduces cancer spread potential: Cancer spreads (metastasizes) when cells become more mobile and invasive.Ivermectin blocked the cancer cells’ ability to migrate and invade in lab tests.It did this partly by reversing “epithelial-mesenchymal transition” (EMT)—a process where cancer cells become more aggressive and spread-prone.Specifically, Ivermectin lowered levels of proteins like vimentin and snail (which promote spread) and may help restore E-cadherin (which keeps cells stuck together).The paper focuses on the Wnt signaling pathway, which is often overactive in breast cancer and drives growth and spread.Ivermectin reduced certain Wnt “signals” (like Wnt5a/b ligands) and a receptor (LRP6), leading to less EMT and potentially slower progression.The effects were stronger in resistant cells.The researchers compared Ivermectin to an approved drug palbociclib (Ibrance), used for similar resistant breast cancers, and found Ivermectin was more effective at blocking some spread-related changes in their tests.CONCLUSION:These lab results suggest Ivermectin has promising anti-growth and anti-spread effects on hormone-therapy-resistant breast cancer cells, possibly by interfering with the Wnt pathway and EMT.My Take…I always get asked - how can Ivermectin possibly treat cancer if it’s an anti-parasitic?The answer is: Ivermectin is a LOT MORE than just an anti-parasitic.Ivermectin has extensive anti-neoplastic properties!