

Asoybean shoot with emerald-green leaves and full pods stands gracefully at the center of a wreath of small, light purple flowers, symbolizing soybean's place as a shining star on the world agricultural product stage. In the featured article, Zhao et al. (pages 3–6) expressed GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR3 and GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR-INTERACTING FACTOR1 from a single construct separated by a small intergenic spacer, during soybean transformation. This construct enhanced the transformation efficiency, opening up a new avenue for soybean research and crop breeding.
Brief Communications
A highly efficient soybean transformation system using GRF3-GIF1 chimeric protein
Ying Zhao, Peng Cheng, Ying Liu, Chunyan Liu, Zhenbang Hu, Dawei Xin, Xiaoxia Wu, Mingliang Yang, Qingshan Chen
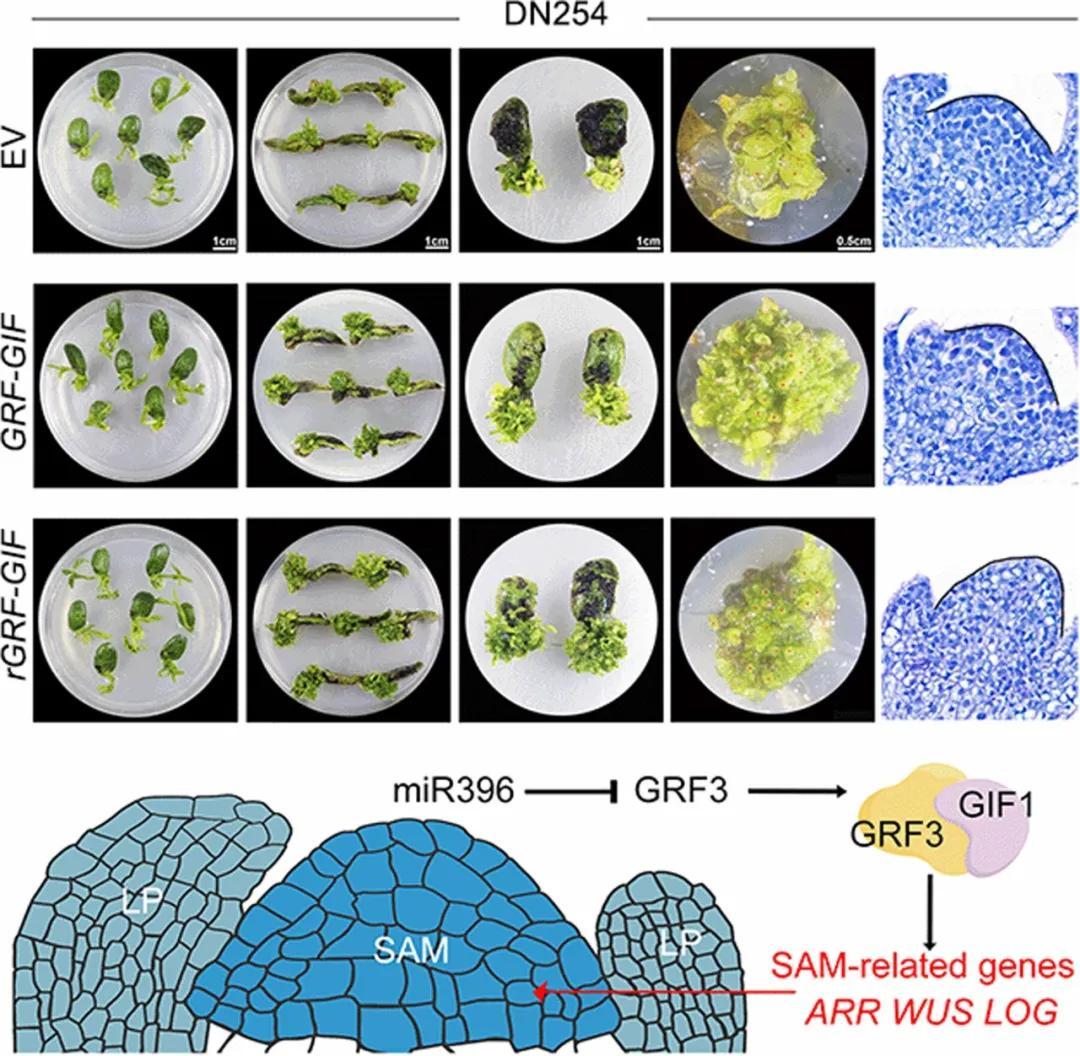
Expression ofGRF3-GIF1chimera significantly enhanced regeneration and transformation efficiency in soybean, increasing the number of transformable cultivars. Moreover,GmGRF3-GIF1can be combined with CRISPR/Cas9 for highly effective gene editing.
Efficient gene disruption in polyploid genome by Cas9–Trex2 fusion protein
Wenbo Pan, Chunlei Gao, De Niu, Jinghua Cheng, Jiao Zhang, Xiying Yan, Qiang Long, YaoYao Zhu, Wenjing Sun, Qi Xie, Yuehui He, Xing Wang Deng, Huawei Zhang, Jian Li
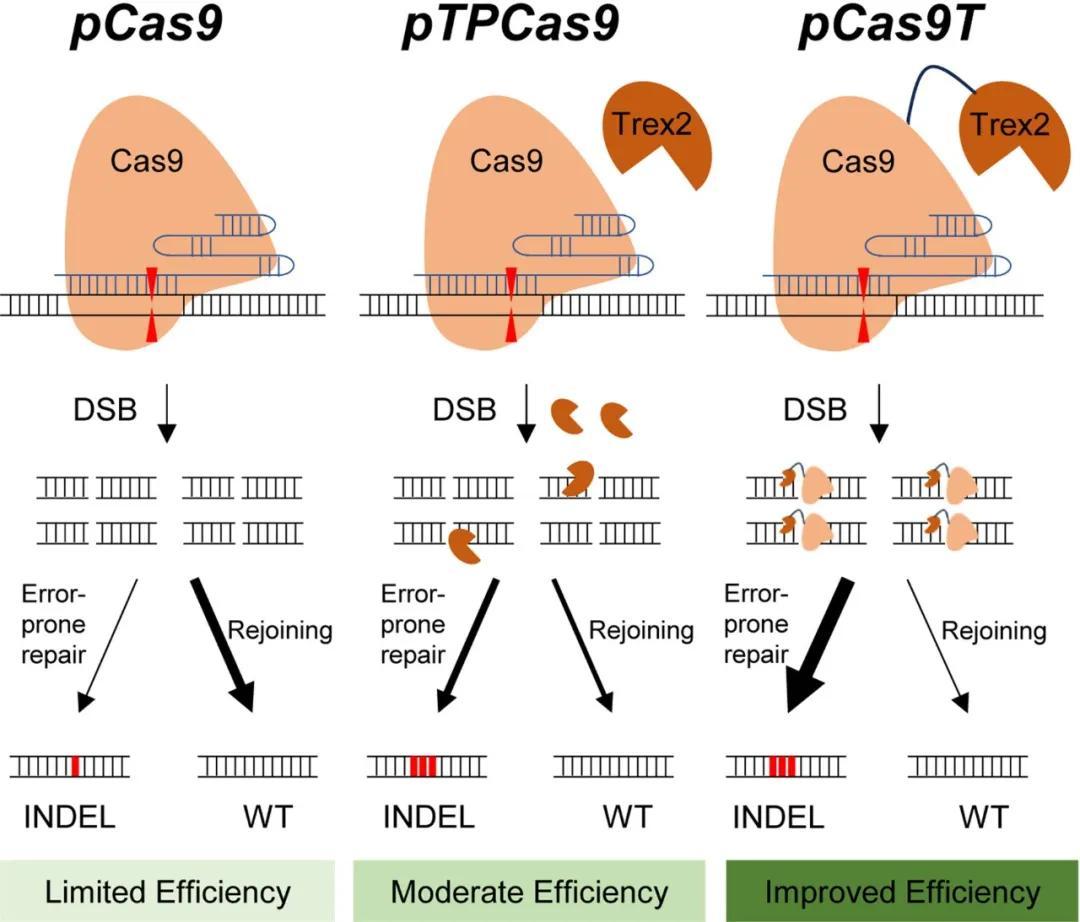
The fusion of the exonuclease Trex2 with the Cas9 protein significantly enhanced the efficiency of genome editing in hexaploid common wheat, particularly for the simultaneous editing of multiple favorable alleles within a single generation, thereby facilitating genome editing-assisted breeding in polyploid crops.
A resurfaced sensor NLR confers new recognition specificity to non-MAX effectors
Tongtong Zhu, Xuefeng Wu, Guixin Yuan, Dongli Wang, Vijai Bhadauria, You-Liang Peng, Junfeng Liu, Xin Zhang

Replacing the HMA domain of the rice (Oryza sativa) immune receptor RGA5 with that of the rice HMA DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN 120 (HMA120) creates a designer RGA5HMA120 that confers resistance toMagnaporthe oryzaeisolates expressing the non-MAX effector geneAVR-Pita, thus enabling the generation of new synthetic resistance genes.
Horizontal transposon transfer during plant terrestrialization
Hao Wang, Zilong Xu, Zhenhua Zhang, Bojian Zhong

During the move to land, plants acquired transposable elements by horizontal transfer from bacteria and fungi and land plants have many long non-coding RNAs derived from retrotransposons acquired by horizontal transposon transfer, including some that are highly expressed and involved in the response to drought stress and abscisic acid.
Abiotic Stress Responses
TaWRKY55–TaPLATZ2 module negatively regulate saline–alkali stress tolerance in wheat
Lin Wei, Xinman Ren, Lumin Qin, Rong Zhang, Minghan Cui, Guangmin Xia, Shuwei Liu
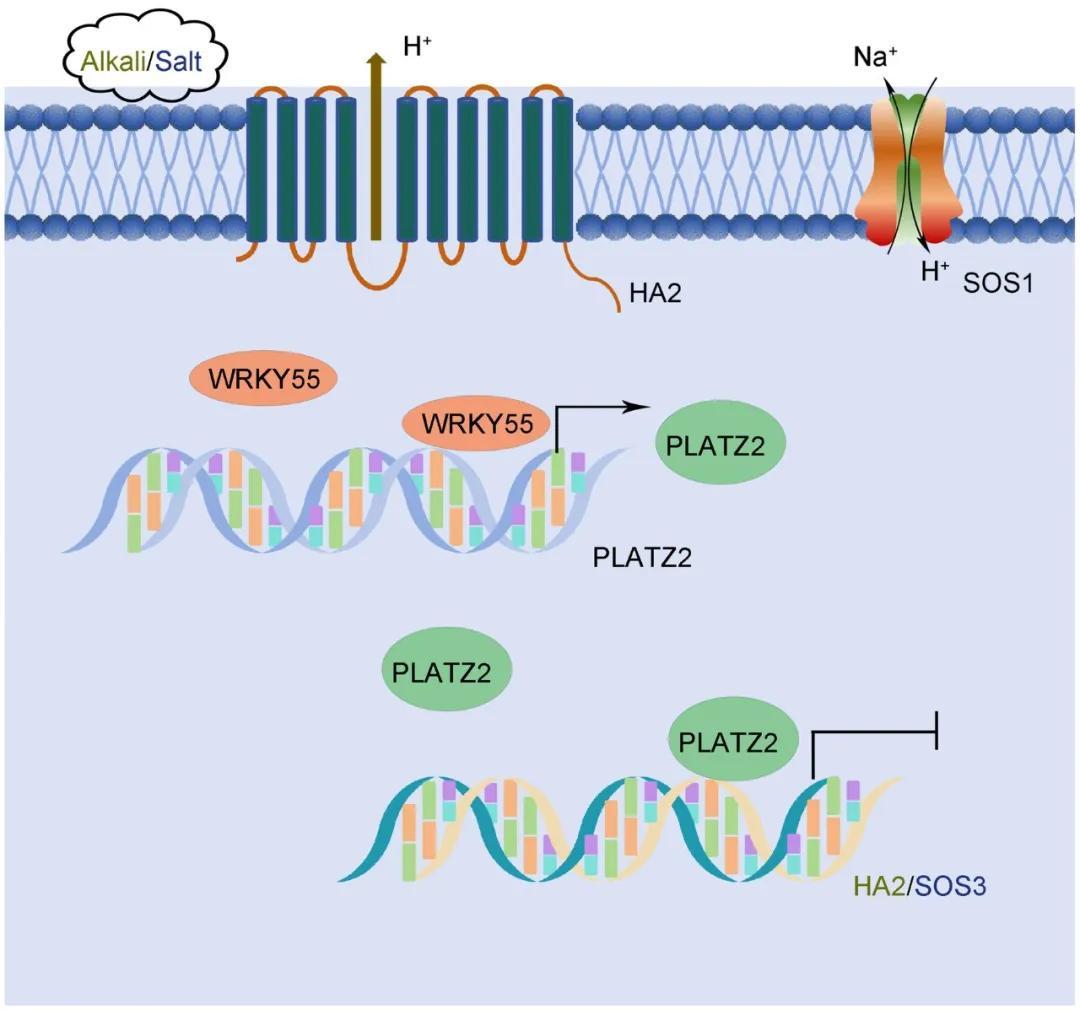
The TaWRKY55-TaPLATZ2 transcription factor module regulates saline-alkali stress responses in wheat by inhibiting the expression of the H+-ATPase geneTaHA2and the salt overly sensitive (SOS) pathway geneTaSOS3.
Cell and Developmental Biology
The MON1–CCZ1 complex plays dual roles in autophagic degradation and vacuolar protein transport in rice
Binglei Zhang, Yihua Wang, Yun Zhu, Tian Pan, Haigang Yan, Xin Wang, Ruonan Jing, Hongming Wu, Fan Wang, Yu Zhang, Xiuhao Bao, Yongfei Wang, Pengcheng Zhang, Yu Chen, Erchao Duan, Xiaohang Han, Gexing Wan, Mengyuan Yan, Xiejun Sun, Cailin Lei, Zhijun Cheng, Zhichao Zhao, Ling Jiang, Yiqun Bao, Yulong Ren, Jianmin Wan

The MONENSIN SENSITIVITY1-CALCIUM CAFFEINE ZINC SENSITIVITY1 (MON1-CCZ1) complex facilitates the membrane fusion between autophagosomes with vacuoles by interacting with AUTOPHAGY-RELATED 8 and has a conserved role as the guanine exchange factor for Rab7 in vacuolar transport pathway.
The regulatory network and critical factors promoting programmed cell death during embryogenesis
An Luo, Ce Shi, Pan Luo, Zifu Zhao, Meng-Xiang Sun

Comparative transcriptome analysis of protease-expressing synchronous two-celled tobacco proembryos with ongoing programmed cell death (PCD) reveals the landscape of gene expression during PCD initiation and major pathways regulating plant PCD.
TavWA1is critical for wheat growth by modulating cell morphology and arrangement
Guowei Chang, Yue Li, Lei Peng, Chuncai Shen, Yipeng Lu, Wan Teng, Yangyang Liu, Yingchun Wang, Weiqi Zhu, Cuimin Liu, Xue He, Yiping Tong, Xueqiang Zhao

In wheat (Triticum aestivum), the von Willebrand factor A domain-containing protein TavWA1-7D regulates growth and yield-related traits by controlling cell morphology and arrangement. TavWA1-7D interacts with the E3 ubiquitin ligase TaVIP1 and TaVIP1 levels are associated with grain size.
Metabolism and Biochemistry
Sulfur metabolism under stress: Oxidized glutathione inhibits methionine biosynthesis by destabilizing the enzyme cystathionine γ-synthase
Yael Hacham, Alex Kaplan, Elad Cohen, Maayan Gal, Rachel Amir
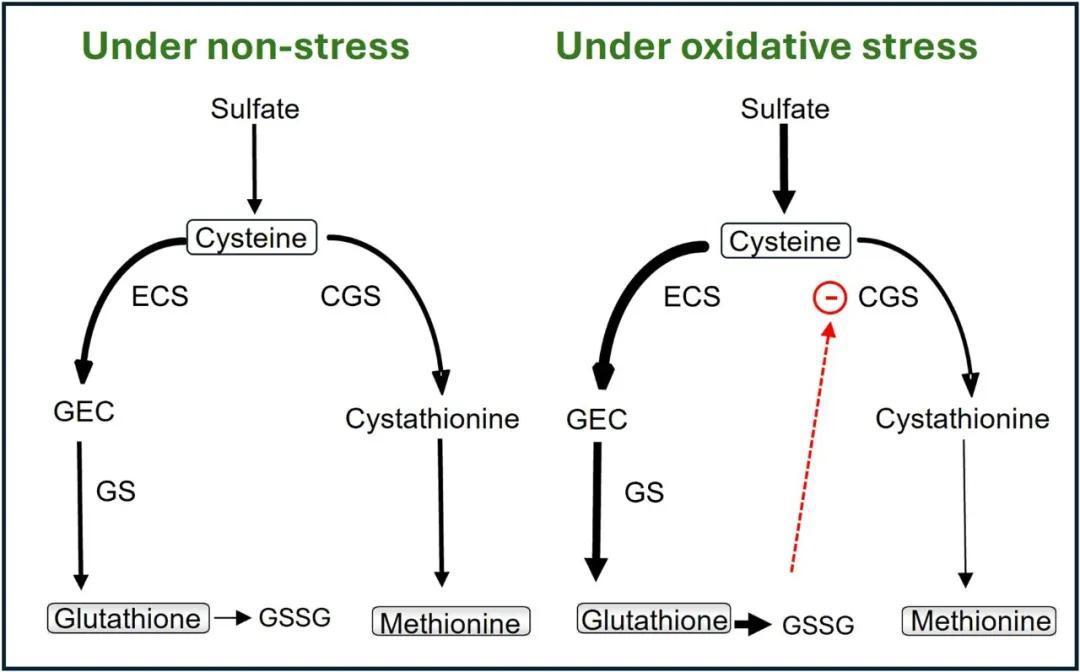
Methionine and glutathione synthesis compete for cysteine. Under oxidative stress, when more glutathione is required to protect the plants, its oxidized form binds the key enzyme of methionine biosynthesis, leading to its degradation. This mechanism helps protect plants but reduces their nutritional value due to lower methionine levels.
Zinc finger transcription factorsBnaSTOP2sregulate sulfur metabolism and conferSclerotinia sclerotiorumresistance inBrassica napus
Lihong Dai, Zhaoqi Xie, Tianxu Ai, Yushun Jiao, Xiaoyi Lian, Angchen Long, Jinyun Zhang, Guangsheng Yang, Dengfeng Hong

The rapeseed (Brassica napus) BnaSTOP2 zinc finger transcription factors form multiple protein complexes that regulate sulfur metabolism and defense responses, influencing sulfur assimilation levels, sulfur compound metabolism in roots, leaves, and siliques, and pathogen resistance.
Molecular Physiology
The PtobZIP55–PtoMYB170 module regulates the wood anatomical and chemical properties ofPopulus tomentosain acclimation to low nitrogen availability
Jiangting Wu, Shurong Deng, Yang Wang, Chenlin Jia, Jia Wei, Mengyan Zhou, Dongyue Zhu, Zhuorong Li, Payam Fayyaz, Zhi-Bin Luo, Jing Zhou, Wenguang Shi

InPopulus tomentosa, low nitrogen induces expression of the transcription factor genePtobZIP55, andPtobZIP55activates expression of another transcription factor gene, PtoMYB170. PtoMYB170 in turn, positively regulates lignin biosynthetic genes to enhance lignin deposition in the secondary xylem.
The ABC transporter SmABCG1 mediates tanshinones export from the peridermic cells ofSalvia miltiorrhizaroot
Yajing Li, Junfeng Chen, Jingyu Zhi, Doudou Huang, Yuchen Zhang, Lei Zhang, Xinyi Duan, Pan Zhang, Shi Qiu, Jiaran Geng, Jingxian Feng, Ke Zhang, Xu Yang, Shouhong Gao, Wenwen Xia, Zheng Zhou, Yuqi Qiao, Bo Li, Qing Li, Tingzhao Li, Wansheng Chen, Ying Xiao

In the medicinal plantSalvia miltiorrhiza, the ABC transporter SmABCG1 mediates export of tanshinones, diterpenoid compounds with medicinal properties, from root peridermic cells, likely prompted by their potential cytotoxicity.
Plant Biotic Interactions
Recognition of a salivary effector by the TNL protein RCSP promotes effector-triggered immunity and systemic resistance inNicotiana benthamiana
Weiwei Rao, Tingting Ma, Jiayuan Cao, Yajun Zhang, Sisi Chen, Shu Lin, Xiaoxiao Liu, Guangcun He, Li Wan
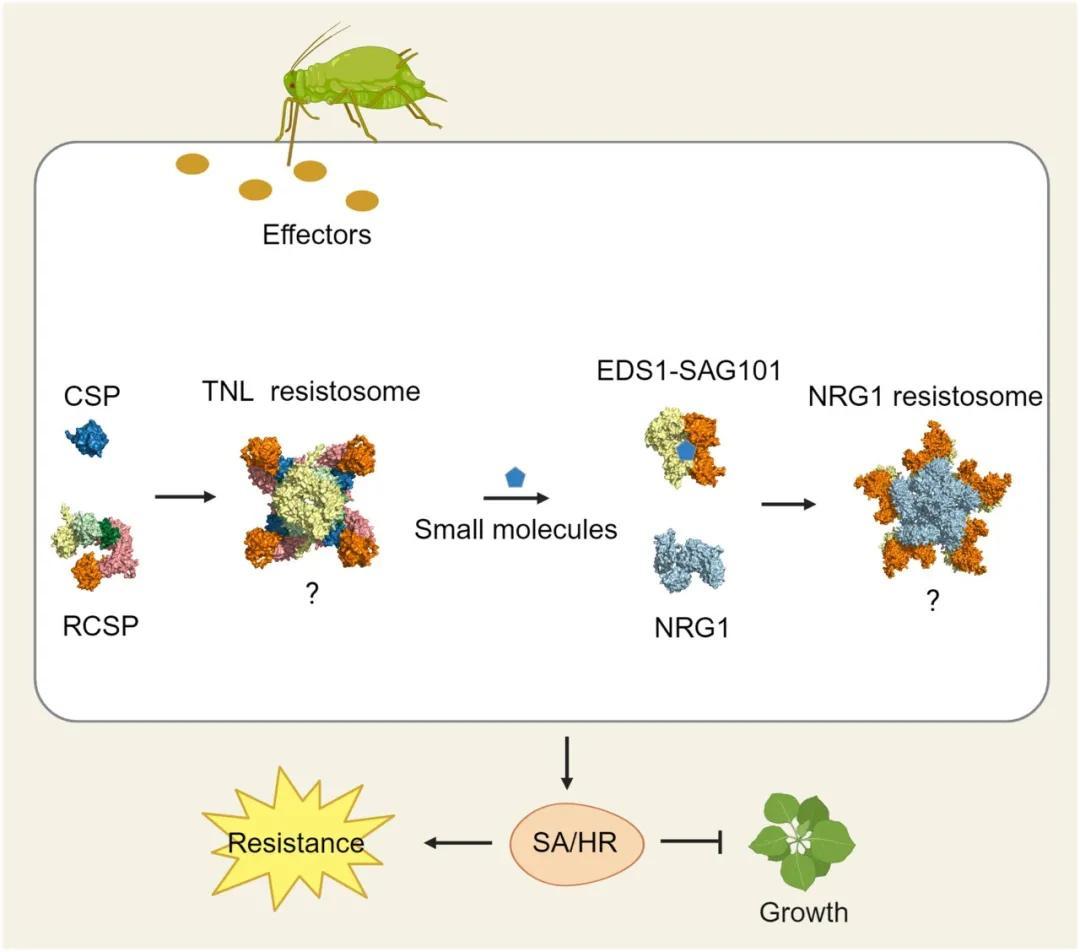
The Toll-interleukin-1 receptor domain nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat protein RCSP recognizes insect salivary effector chemosensory proteins, promoting effector-triggered immunity and systemic resistance inNicotiana benthamiana.
Plant Reproductive Biology
The miR3367–lncRNA67–GhCYP724B module regulates male sterility by modulating brassinosteroid biosynthesis and interacting with Aorf27 inGossypium hirsutum
Anhui Guo, Hushuai Nie, Huijing Li, Bin Li, Cheng Cheng, Kaiyun Jiang, Shengwei Zhu, Nan Zhao, Jinping Hua
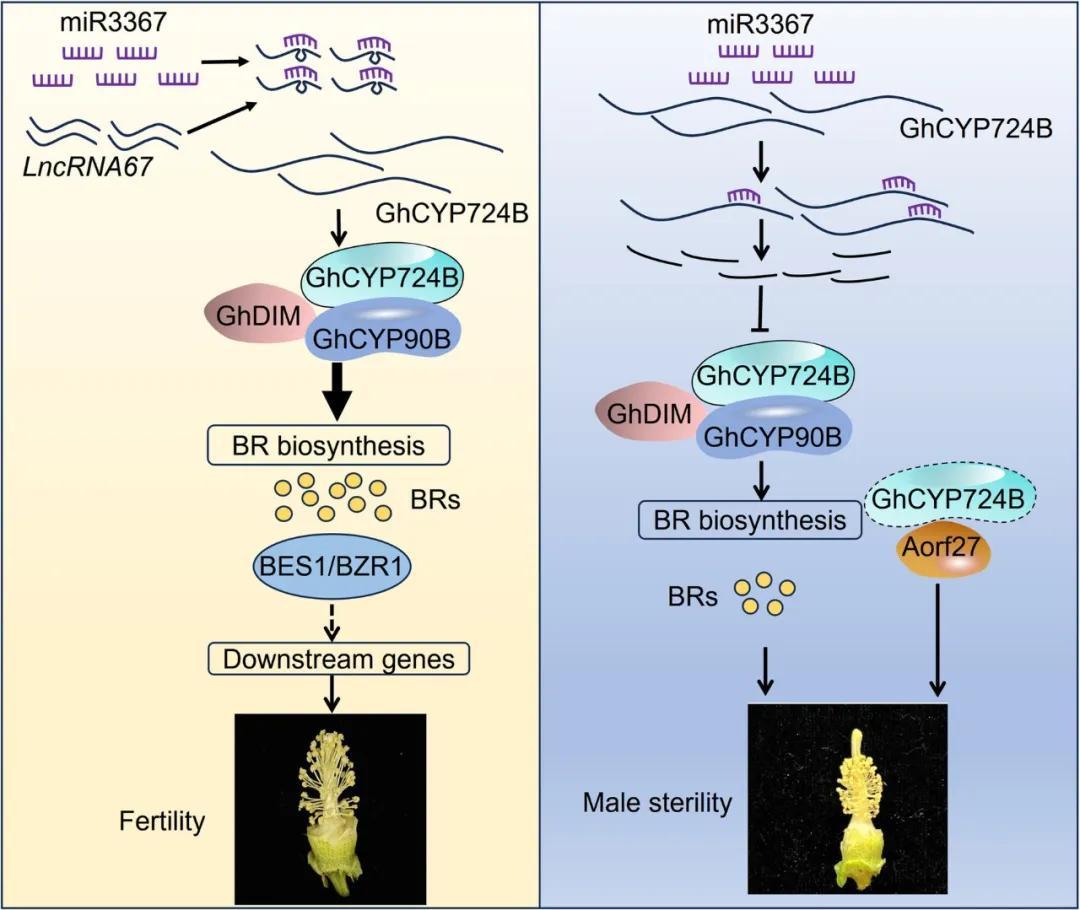
In the fertile cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) line 2074B, the long non-coding RNA lncRNA67 acted as an endogenous target mimic, regulating microRNA-mediated cleavage ofGhCYP724B, encoding a cytochrome P450 that promotes brassinosteroid biosynthesis. In the cytoplasmic male sterile line 2074A, GhCYP724B interacted with a unique chimeric open reading frame, resulting in male sterility.
Acknowledgements
Acknowledgements to Reviewers
The editorial team of JIPB would like to express sincere gratitude to the following reviewers for their diligence and insightful feedback between September 15, 2023, and December 31, 2024. Your invaluable contributions are crucial in maintaining the high standards and quality of our journal. We look forward to your continued support in 2025.
