websocket在前端开发中,是一个必须掌握的技术!你可以不用,但必须掌握!
前几天,就遇到这样一个需求,要求界面的数据通过websocket实时推送,并且必须支持断网重连、自动心跳!
自动心跳是定期向服务端发送小型数据包,如果一段时间内服务端没有收到心跳响应,系统可能会断开连接。
websokect的API非常简单
// 创建ws连接const ws = new WebSocket('ws://localhost:8080/test');ws.onopen = function() { console.log('WebSocket 连接已经建立。'); ws.send('Hello, server!');};ws.onmessage = function(event) { console.log('收到服务器消息:', event.data);};ws.onerror = function(event) { console.error('WebSocket 连接出现错误:', event);};ws.onclose = function() { console.log('WebSocket 连接已经关闭。');}但是,要封装一个支持断网重连、自动心跳的websokect没有那么容易!
封装成功演示核心优势我们先看我封装的websokect,首先,最重要的,它的使用方法和官方Api完全一致!零学习成本,上手即用!
import WebSocketClient from "./WebSocketClient"// 创建实例const ws = new WebSocketClient('ws://localhost:3200');// 连接ws.connect()// 同原生方法ws.onclose(()=>{})// 同原生方法ws.onerror(()=>{})// 同原生方法ws.onmessage(()=>{ // 同原生方法 ws.send("自定义发送的数据")})// 同原生方法ws.onopen(()=>{})// 关闭连接ws.close()效果演示后端服务创建我们先使用node创建一个后端服务,安装ws库:
npm install ws创建node index.js文件,引入WebSocket 服务器
const WebSocket = require("ws");const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ port: 3200 });console.log("服务运行在http://localhost:3200/");wss.on("connection", (ws) => { console.log("[服务器]:客官您来了~里边请"); ws.send(`[websocket云端]您已经连接云端!数据推送中!`); let index = 1; const interval = setInterval(() => { ws.send(`[websocket]数据推送第${index}次`); index ++ }, 1000 * 10); ws.on("close", () => { clearInterval(interval); // 清除定时器 console.log("[服务器]:客官下次再来呢~"); });});我们启动这个服务
node index.js现在,我们在前端服务内进行连接测试
前端websokect测试我们先写前端的相关逻辑
import { WebSocketClient } from '@/utils/dataDispatcher/WebSocketClient';const ws = new WebSocketClient('ws://localhost:3200');// 连接ws.connect();// 同原生方法ws.onclose(() => {});// 同原生方法ws.onerror(() => {});// 同原生方法ws.onmessage(() => { // 同原生方法 ws.send('自定义发送的数据');});// 同原生方法ws.onopen(() => {});启动项目,我们会发现控制台已经有了提示
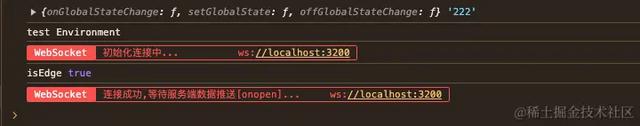
心跳验证:
等待一段时间后,我们可以看到ws连接里,前端已经发送了多次心跳数据
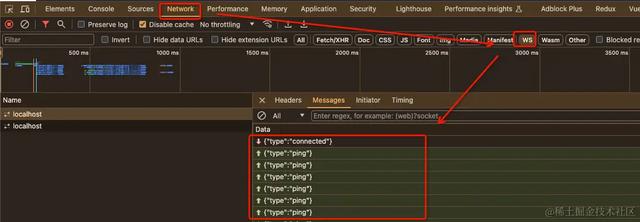
服务端与客户端也一直在进行数据交互

断网重连验证:
可以看到,当我们断开服务端的时候,断网重连被自动触发。
 技术路线基本框架搭建export WebSocketClient { // #socket链接 private url = ''; // #socket实例 private socket: WebSocket | null = null; constructor(url: string) { super(); this.url = url; } // >消息发送 public send(message: string): void { if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { this.socket.send(message); } else { console.error('[WebSocket] 未连接'); } } // !初始化连接 public connect(): void { if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { return; } this.socket = new WebSocket(this.url); // !websocket连接成功 this.socket.onopen = event => { console.log(`连接成功,等待服务端数据推送[onopen]...`); }; this.socket.onmessage = event => { }; this.socket.onclose = event => { console.log(`连接断开[onclose]...`); }; this.socket.onerror = event => { console.log(`连接异常[onerror]...`); }; } // >关闭连接 public close(): void { if (this.socket) { this.socket.close(); this.socket = null; } }}
技术路线基本框架搭建export WebSocketClient { // #socket链接 private url = ''; // #socket实例 private socket: WebSocket | null = null; constructor(url: string) { super(); this.url = url; } // >消息发送 public send(message: string): void { if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { this.socket.send(message); } else { console.error('[WebSocket] 未连接'); } } // !初始化连接 public connect(): void { if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { return; } this.socket = new WebSocket(this.url); // !websocket连接成功 this.socket.onopen = event => { console.log(`连接成功,等待服务端数据推送[onopen]...`); }; this.socket.onmessage = event => { }; this.socket.onclose = event => { console.log(`连接断开[onclose]...`); }; this.socket.onerror = event => { console.log(`连接异常[onerror]...`); }; } // >关闭连接 public close(): void { if (this.socket) { this.socket.close(); this.socket = null; } }}上述代码借助官方API实现了一个基本的 WebSocket 客户端,具有以下功能:
初始化连接并处理各种 WebSocket 事件(打开、消息、关闭、错误)。发送消息到服务器。关闭连接。现在,我们开始逐步完善代码,进行封装。
断网重连封装export WebSocketClient{ // #socket链接 private url = ''; // #socket实例 private socket: WebSocket | null = null; // #重连次数 private reconnectAttempts = 0; // #最大重连数 private maxReconnectAttempts = 5; // #重连间隔 private reconnectInterval = 10000; // 10 seconds constructor(url: string) { super(); this.url = url; } // >消息发送 public send(message: string): void { if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { this.socket.send(message); } else { console.error('[WebSocket] 未连接'); } } // !初始化连接 public connect(): void { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { console.log(`初始化连接中...`); } if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { return; } this.socket = new WebSocket(this.url); // !websocket连接成功 this.socket.onopen = event => { // 重置重连尝试成功连接 this.reconnectAttempts = 0; console.log(`连接成功,等待服务端数据推送[onopen]...`); }; this.socket.onmessage = event => { }; this.socket.onclose = event => { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { console.log(`连接断开[onclose]...`); } if (!this.stopWs) { this.handleReconnect(); } }; this.socket.onerror = event => { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { console.log(`连接异常[onerror]...`); } }; } // > 断网重连逻辑 private handleReconnect(): void { if (this.reconnectAttempts < this.maxReconnectAttempts) { this.reconnectAttempts++; console.log(`尝试重连... (${this.reconnectAttempts}/${this.maxReconnectAttempts})`); setTimeout(() => { this.connect(); }, this.reconnectInterval); } else { console.log(`最大重连失败,终止重连: ${this.url}`); } } // >关闭连接 public close(): void { if (this.socket) { this.socket.close(); this.socket = null; } }}上述代码添加了自动断网重连的机制。其核心逻辑在于以下几个方面:
记录重连次数:通过 reconnectAttempts 属性记录当前已经尝试重连的次数。设置最大重连次数:通过 maxReconnectAttempts 属性设置允许的最大重连次数。重连逻辑:在 onclose 和 onerror 事件中调用重连处理函数 handleReconnect。重连间隔:通过 reconnectInterval 属性设置每次重连的间隔时间,可以在每次重连时增加间隔以实现指数退避。初始化连接并处理事件
在 connect 方法中,初始化 WebSocket 连接并为其设置事件处理函数。特别关注 onclose 和 onerror 事件,在连接关闭和出现错误时调用重连逻辑。
public connect(): void { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { console.log(`初始化连接中...`); } if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { return; } this.socket = new WebSocket(this.url); this.socket.onopen = (event: Event) => { this.reconnectAttempts = 0; console.log(`连接成功,等待服务端数据推送[onopen]...`); }; this.socket.onclose = (event: CloseEvent) => { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { console.log(`连接断开[onclose]...`); } this.handleReconnect(); }; this.socket.onerror = (event: Event) => { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { console.log(`连接异常[onerror]...`); } this.handleReconnect(); };}处理重连逻辑
在 handleReconnect 方法中,实现了实际的重连逻辑。该方法会递增 reconnectAttempts,检查是否达到最大重连次数,如果没有达到,则在指定的重连间隔后再次调用 connect 方法尝试重连。
private handleReconnect(): void { if (this.reconnectAttempts < this.maxReconnectAttempts) { this.reconnectAttempts++; console.log(`尝试重连... (${this.reconnectAttempts}/${this.maxReconnectAttempts})`); setTimeout(() => { this.connect(); }, this.reconnectInterval * this.reconnectAttempts); // 重连间隔可以增加,例如指数退避 } else { console.log(`最大重连失败,终止重连: ${this.url}`); }}关闭连接
在 close 方法中,手动关闭 WebSocket 连接并将 socket 设置为 null。
public close(): void { if (this.socket) { this.socket.close(); this.socket = null; }}自动心跳封装自动心跳(Automatic Heartbeat)是一种在网络通信中常用的机制,用于维持连接的活跃状态,检测连接是否仍然有效,并及时发现和处理连接断开或故障的情况。心跳机制通过定期发送“心跳”消息(通常是一个简单的 ping 或者 pong 消息)来确认连接双方的状态。
实现自动心跳的基本思路
发送心跳消息:在 WebSocket 连接建立后,启动一个定时器,定期发送心跳消息到服务器。接收心跳响应:服务器收到心跳消息后返回响应,客户端接收到响应后重置定时器。检测心跳超时:如果在指定时间内没有收到心跳响应,则认为连接断开,进行重连。export WebSocketClient { // #socket链接 private url = ''; // #socket实例 private socket: WebSocket | null = null; // #重连次数 private reconnectAttempts = 0; // #最大重连数 private maxReconnectAttempts = 5; // #重连间隔 private reconnectInterval = 10000; // 10 seconds // #发送心跳数据间隔 private heartbeatInterval = 1000 * 30; // #计时器id private heartbeatTimer?: NodeJS.Timeout; // #彻底终止ws private stopWs = false; // *构造函数 constructor(url: string) { super(); this.url = url; } // >消息发送 public send(message: string): void { if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { this.socket.send(message); } else { console.error('[WebSocket] 未连接'); } } // !初始化连接 public connect(): void { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { console.log('WebSocket', `初始化连接中...`); } if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { return; } this.socket = new WebSocket(this.url); // !websocket连接成功 this.socket.onopen = event => { this.stopWs = false; // 重置重连尝试成功连接 this.reconnectAttempts = 0; // 在连接成功时停止当前的心跳检测并重新启动 this.startHeartbeat(); console.log(`连接成功,等待服务端数据推送[onopen]...`); }; this.socket.onmessage = event => { this.dispatchEvent('message', event); this.startHeartbeat(); }; this.socket.onclose = event => { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { console.log(`连接断开[onclose]...`); } if (!this.stopWs) { this.handleReconnect(); } }; this.socket.onerror = event => { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { console.log(`连接异常[onerror]...`); } this.closeHeartbeat(); }; } // > 断网重连逻辑 private handleReconnect(): void { if (this.reconnectAttempts < this.maxReconnectAttempts) { this.reconnectAttempts++; console.log('WebSocket', `尝试重连...`); setTimeout(() => { this.connect(); }, this.reconnectInterval); } else { this.closeHeartbeat(); console.log(`最大重连失败,终止重连: ${this.url}`); } } // >关闭连接 public close(): void { if (this.socket) { this.stopWs = true; this.socket.close(); this.socket = null; } this.closeHeartbeat(); } // >开始心跳检测 -> 定时发送心跳消息 private startHeartbeat(): void { if (this.stopWs) return; if (this.heartbeatTimer) { this.closeHeartbeat(); } this.heartbeatTimer = setInterval(() => { if (this.socket) { this.socket.send(JSON.stringify({ type: 'heartBeat', data: {} })); console.log('WebSocket', '送心跳数据...'); } else { console.error('[WebSocket] 未连接'); } }, this.heartbeatInterval); } // >关闭心跳 private closeHeartbeat(): void { clearInterval(this.heartbeatTimer); this.heartbeatTimer = undefined; }}上述代码通过定时发送心跳消息来实现自动心跳机制,并结合断网重连逻辑来确保 WebSocket 连接的稳定性。
心跳机制的实现原理简析:
在连接成功时启动心跳检测在 connect() 方法中,当 WebSocket 连接成功(onopen 事件触发)时,调用 startHeartbeat() 方法。
this.socket.onopen = event => { this.stopWs = false; this.reconnectAttempts = 0; this.startHeartbeat(); console.log(`连接成功,等待服务端数据推送[onopen]...`);};定时发送心跳消息startHeartbeat() 方法启动一个定时器,每隔 heartbeatInterval 时间(30秒)发送一次心跳消息。
private startHeartbeat(): void { if (this.stopWs) return;if (this.heartbeatTimer) { this.closeHeartbeat();}this.heartbeatTimer = setInterval(() => { if (this.socket) { this.socket.send(JSON.stringify({ type: 'heartBeat', data: {} })); console.log('WebSocket', '发送心跳数据...'); } else { console.error('[WebSocket] 未连接'); }}, this.heartbeatInterval);}停止心跳检测closeHeartbeat() 方法用于停止心跳检测,清除定时器。
private closeHeartbeat(): void { clearInterval(this.heartbeatTimer); this.heartbeatTimer = undefined;}在连接断开或发生错误时停止心跳检测在 onclose 和 onerror 事件中调用 closeHeartbeat(),停止心跳检测。
this.socket.onclose = event => { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { console.log(`连接断开[onclose]...`); } if (!this.stopWs) { this.handleReconnect(); }};this.socket.onerror = event => { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { console.log(`连接异常[onerror]...`); } this.closeHeartbeat();};如何触发原生函数现在,我们已经基本完成了功能的封装,那么,我们如何在外部调用原生的websokectApi呢?非常简单,借助几个自定义的生命周期函数即可!
import { EventDispatcher } from './dispatcher';export WebSocketClient extends EventDispatcher { //... constructor(url: string) { super(); this.url = url; } // >生命周期钩子 onopen(callBack: Function) { this.addEventListener('open', callBack); } onmessage(callBack: Function) { this.addEventListener('message', callBack); } onclose(callBack: Function) { this.addEventListener('close', callBack); } onerror(callBack: Function) { this.addEventListener('error', callBack); } // !初始化连接 public connect(): void { // ... // !websocket连接成功 this.socket.onopen = event => { // ... this.dispatchEvent('open', event); }; this.socket.onmessage = event => { this.dispatchEvent('message', event); this.startHeartbeat(); }; this.socket.onclose = event => { // ... this.dispatchEvent('close', event); }; this.socket.onerror = event => { // ... this.closeHeartbeat(); this.dispatchEvent('error', event); }; } // >关闭连接 public close(): void { if (this.socket) { this.stopWs = true; this.socket.close(); this.socket = null; this.removeEventListener('open'); this.removeEventListener('message'); this.removeEventListener('close'); this.removeEventListener('error'); } this.closeHeartbeat(); } // ...}当原生的onclose、onopen方法触发时,会通过dispatchEvent触发相应的调度,进而触发通过addEventListener绑定的生命周期函数!
注意,这里的this.dispatchEvent方法,addEventListener方法都是通过类继承EventDispatcher方法获得的!
EventDispatcher源码如下:
export EventDispatcher { private listeners: { [type: string]: Function[] } = {}; protected addEventListener(type: string, listener: Function) { if (!this.listeners[type]) { this.listeners[type] = []; } if (this.listeners[type].indexOf(listener) === -1) { this.listeners[type].push(listener); } } protected removeEventListener(type: string) { this.listeners[type] = []; } protected dispatchEvent(type: string, data: any) { const listenerArray = this.listeners[type] || []; if (listenerArray.length === 0) return; listenerArray.forEach(listener => { listener.call(this, data); }); }}关于EventDispatcher的实现原理,请参考博主的其他文章:
juejin.cn/post/735851…
完整代码ts版本import { EventDispatcher } from './dispatcher';export WebSocketClient extends EventDispatcher { // #socket链接 private url = ''; // #socket实例 private socket: WebSocket | null = null; // #重连次数 private reconnectAttempts = 0; // #最大重连数 private maxReconnectAttempts = 5; // #重连间隔 private reconnectInterval = 10000; // 10 seconds // #发送心跳数据间隔 private heartbeatInterval = 1000 * 30; // #计时器id private heartbeatTimer?: NodeJS.Timeout; // #彻底终止ws private stopWs = false; // *构造函数 constructor(url: string) { super(); this.url = url; } // >生命周期钩子 onopen(callBack: Function) { this.addEventListener('open', callBack); } onmessage(callBack: Function) { this.addEventListener('message', callBack); } onclose(callBack: Function) { this.addEventListener('close', callBack); } onerror(callBack: Function) { this.addEventListener('error', callBack); } // >消息发送 public send(message: string): void { if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { this.socket.send(message); } else { console.error('[WebSocket] 未连接'); } } // !初始化连接 public connect(): void { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { this.log('WebSocket', `初始化连接中... ${this.url}`); } if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { return; } this.socket = new WebSocket(this.url); // !websocket连接成功 this.socket.onopen = event => { this.stopWs = false; // 重置重连尝试成功连接 this.reconnectAttempts = 0; // 在连接成功时停止当前的心跳检测并重新启动 this.startHeartbeat(); this.log('WebSocket', `连接成功,等待服务端数据推送[onopen]... ${this.url}`); this.dispatchEvent('open', event); }; this.socket.onmessage = event => { this.dispatchEvent('message', event); this.startHeartbeat(); }; this.socket.onclose = event => { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { this.log('WebSocket', `连接断开[onclose]... ${this.url}`); } if (!this.stopWs) { this.handleReconnect(); } this.dispatchEvent('close', event); }; this.socket.onerror = event => { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { this.log('WebSocket', `连接异常[onerror]... ${this.url}`); } this.closeHeartbeat(); this.dispatchEvent('error', event); }; } // > 断网重连逻辑 private handleReconnect(): void { if (this.reconnectAttempts < this.maxReconnectAttempts) { this.reconnectAttempts++; this.log('WebSocket', `尝试重连... (${this.reconnectAttempts}/${this.maxReconnectAttempts}) ${this.url}`); setTimeout(() => { this.connect(); }, this.reconnectInterval); } else { this.closeHeartbeat(); this.log('WebSocket', `最大重连失败,终止重连: ${this.url}`); } } // >关闭连接 public close(): void { if (this.socket) { this.stopWs = true; this.socket.close(); this.socket = null; this.removeEventListener('open'); this.removeEventListener('message'); this.removeEventListener('close'); this.removeEventListener('error'); } this.closeHeartbeat(); } // >开始心跳检测 -> 定时发送心跳消息 private startHeartbeat(): void { if (this.stopWs) return; if (this.heartbeatTimer) { this.closeHeartbeat(); } this.heartbeatTimer = setInterval(() => { if (this.socket) { this.socket.send(JSON.stringify({ type: 'heartBeat', data: {} })); this.log('WebSocket', '送心跳数据...'); } else { console.error('[WebSocket] 未连接'); } }, this.heartbeatInterval); } // >关闭心跳 private closeHeartbeat(): void { clearInterval(this.heartbeatTimer); this.heartbeatTimer = undefined; }}jsclass Log { private static console = true; log(title: string, text: string) { if (!Log.console) return; if (import.meta.env.MODE === 'production') return; const color = '#ff4d4f'; console.log( `%c ${title} %c ${text} %c`, `background:${color};border:1px solid ${color}; padding: 1px; border-radius: 2px 0 0 2px; color: #fff;`, `border:1px solid ${color}; padding: 1px; border-radius: 0 2px 2px 0; color: ${color};`, 'background:transparent' ); } closeConsole() { Log.console = false; }}export EventDispatcher extends Log { private listeners: { [type: string]: Function[] } = {}; protected addEventListener(type: string, listener: Function) { if (!this.listeners[type]) { this.listeners[type] = []; } if (this.listeners[type].indexOf(listener) === -1) { this.listeners[type].push(listener); } } protected removeEventListener(type: string) { this.listeners[type] = []; } protected dispatchEvent(type: string, data: any) { const listenerArray = this.listeners[type] || []; if (listenerArray.length === 0) return; listenerArray.forEach(listener => { listener.call(this, data); }); }}js版本export WebSocketClient extends EventDispatcher { // #socket链接 url = ''; // #socket实例 socket = null; // #重连次数 reconnectAttempts = 0; // #最大重连数 maxReconnectAttempts = 5; // #重连间隔 reconnectInterval = 10000; // 10 seconds // #发送心跳数据间隔 heartbeatInterval = 1000 * 30; // #计时器id heartbeatTimer = undefined; // #彻底终止ws stopWs = false; // *构造函数 constructor(url) { super(); this.url = url; } // >生命周期钩子 onopen(callBack) { this.addEventListener('open', callBack); } onmessage(callBack) { this.addEventListener('message', callBack); } onclose(callBack) { this.addEventListener('close', callBack); } onerror(callBack) { this.addEventListener('error', callBack); } // >消息发送 send(message) { if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { this.socket.send(message); } else { console.error('[WebSocket] 未连接'); } } // !初始化连接 connect() { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { this.log('WebSocket', `初始化连接中... ${this.url}`); } if (this.socket && this.socket.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) { return; } this.socket = new WebSocket(this.url); // !websocket连接成功 this.socket.onopen = event => { this.stopWs = false; // 重置重连尝试成功连接 this.reconnectAttempts = 0; // 在连接成功时停止当前的心跳检测并重新启动 this.startHeartbeat(); this.log('WebSocket', `连接成功,等待服务端数据推送[onopen]... ${this.url}`); this.dispatchEvent('open', event); }; this.socket.onmessage = event => { this.dispatchEvent('message', event); this.startHeartbeat(); }; this.socket.onclose = event => { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { this.log('WebSocket', `连接断开[onclose]... ${this.url}`); } if (!this.stopWs) { this.handleReconnect(); } this.dispatchEvent('close', event); }; this.socket.onerror = event => { if (this.reconnectAttempts === 0) { this.log('WebSocket', `连接异常[onerror]... ${this.url}`); } this.closeHeartbeat(); this.dispatchEvent('error', event); }; } // > 断网重连逻辑 handleReconnect() { if (this.reconnectAttempts < this.maxReconnectAttempts) { this.reconnectAttempts++; this.log('WebSocket', `尝试重连... (${this.reconnectAttempts}/${this.maxReconnectAttempts}) ${this.url}`); setTimeout(() => { this.connect(); }, this.reconnectInterval); } else { this.closeHeartbeat(); this.log('WebSocket', `最大重连失败,终止重连: ${this.url}`); } } // >关闭连接 close() { if (this.socket) { this.stopWs = true; this.socket.close(); this.socket = null; this.removeEventListener('open'); this.removeEventListener('message'); this.removeEventListener('close'); this.removeEventListener('error'); } this.closeHeartbeat(); } // >开始心跳检测 -> 定时发送心跳消息 startHeartbeat() { if (this.stopWs) return; if (this.heartbeatTimer) { this.closeHeartbeat(); } this.heartbeatTimer = setInterval(() => { if (this.socket) { this.socket.send(JSON.stringify({ type: 'heartBeat', data: {} })); this.log('WebSocket', '送心跳数据...'); } else { console.error('[WebSocket] 未连接'); } }, this.heartbeatInterval); } // >关闭心跳 closeHeartbeat() { clearInterval(this.heartbeatTimer); this.heartbeatTimer = undefined; }}class Log { static console = true; log(title, text) { if (!Log.console) return; if (import.meta.env.MODE === 'production') return; const color = '#ff4d4f'; console.log( `%c ${title} %c ${text} %c`, `background:${color};border:1px solid ${color}; padding: 1px; border-radius: 2px 0 0 2px; color: #fff;`, `border:1px solid ${color}; padding: 1px; border-radius: 0 2px 2px 0; color: ${color};`, 'background:transparent' ); } closeConsole() { Log.console = false; }}export EventDispatcher extends Log { listeners = {}; addEventListener(type, listener) { if (!this.listeners[type]) { this.listeners[type] = []; } if (this.listeners[type].indexOf(listener) === -1) { this.listeners[type].push(listener); } } removeEventListener(type) { this.listeners[type] = []; } dispatchEvent(type, data) { const listenerArray = this.listeners[type] || []; if (listenerArray.length === 0) return; listenerArray.forEach(listener => { listener.call(this, data); }); }}总结这篇文章封装了weboskect,完美支持了断网重连、自动心跳的功能,且完全兼容原生写法,无任何学习负担,开开箱即用!但美中不足的是,断网重连时间、心跳数据内容目前都是写死的,大家可以根据自己的情况做一些更改,让它更灵活!
作者:石小石Orz链接:https://juejin.cn/post/7371365854012276747
