

Grapes, first written about in The Book of Songs, have been cultivated for millennia and have become globally valued as a fresh fruit and for making wine. The cover depicts grapevines growing along the coast in Shenzhen, China, where they produce a bountiful harvest brought by the gentle breeze. However, these grapevines are not delicate––they can withstand the sea wind and the splashing of seawater, symbolizing the tenacious vitality of grapes that are adapted to the coastal environment. The population genomics study by Zhang et al. (pages 1408–1426) offers valuable insights for breeding salt-tolerant grape rootstocks and identifies key structural variations, advancing horticulture of this economically and culturally significant crop.
Commentary
DGK5-mediated phosphatidic acid homeostasis interplays with reactive oxygen species in plant immune signaling
Dian Wang, Minhang Yuan, Yamei Zhuang, Xiu-Fang Xin, Guang Qi
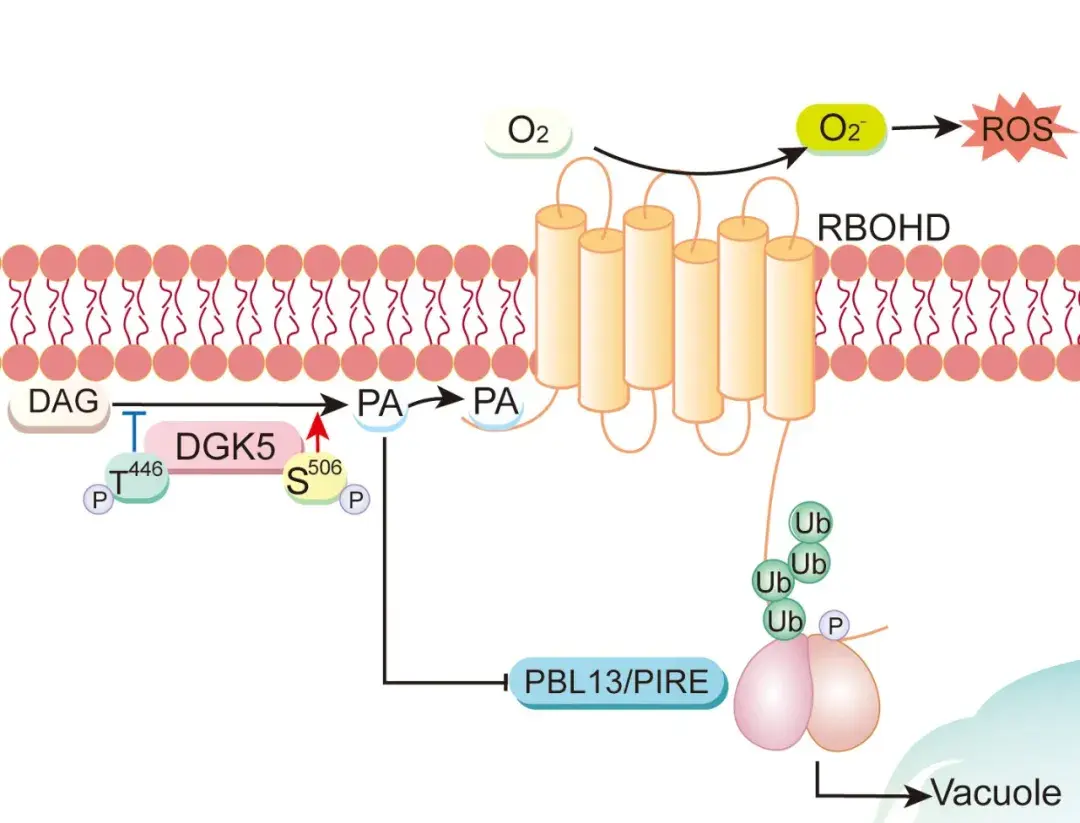
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and phosphatidic acid (PA) are important second messengers in plant immunity. PA binding to RBOHD, an NADPH oxidase responsible for ROS production, enhances RBOHD stability and promotes ROS production. Distinct phosphorylation of the lipid kinase DGK5 optimizes the PA burst in regulating ROS production.
Brief Communications
TaMYB72 directly activates the expression ofTaFTto promote heading and enhance grain yield traits in wheat (Triticum aestivumL.)
Lifen Wu, Zhencheng Xie, Danping Li, Yaoyu Chen, Chuan Xia, Xiuying Kong, Xu Liu, Lichao Zhang

Heading date, grain number per spike, and grain weight are crucial traits affecting yield and adaptability in wheat. The transcription factor TaMYB72 is an important regulator of wheat grain yield and its knock-out mutants can be used as germplasm resources for wheat improvement.
Apple SINA11-JAZ2 module is involved in jasmonate signaling response
Di Ai, Lei Zhao, Chun-Xiang You, Yuepeng Han, Jian-Ping An
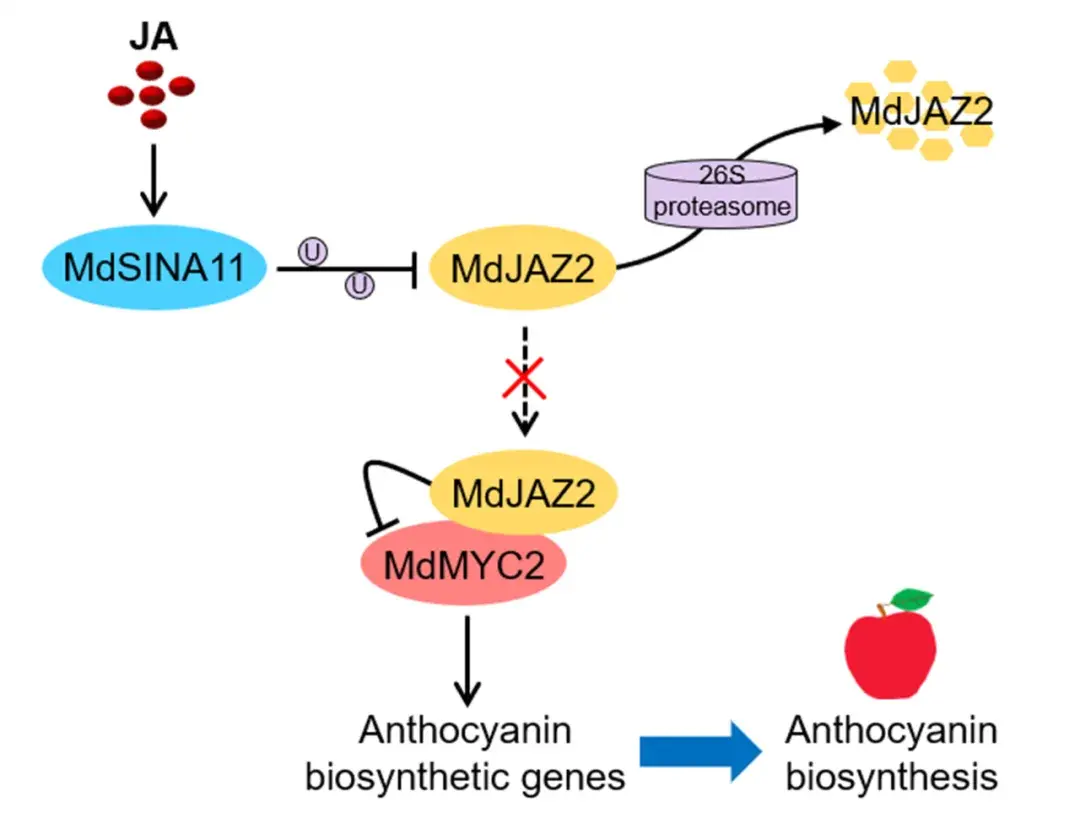
The E3 ubiquitin ligase MdSINA11 targets the jasmonate ZIM domain protein MdJAZ2 for ubiquitination and degradation through the 26S proteasome pathway, thereby initiating jasmonate signaling and jasmonic acid–triggered anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple.
Review Article
Small particles, big effects: How nanoparticles can enhance plant growth in favorable and harsh conditions
Jie Wang, Honghong Wu, Yichao Wang, Wuwei Ye, Xiangpei Kong, Zujun Yin
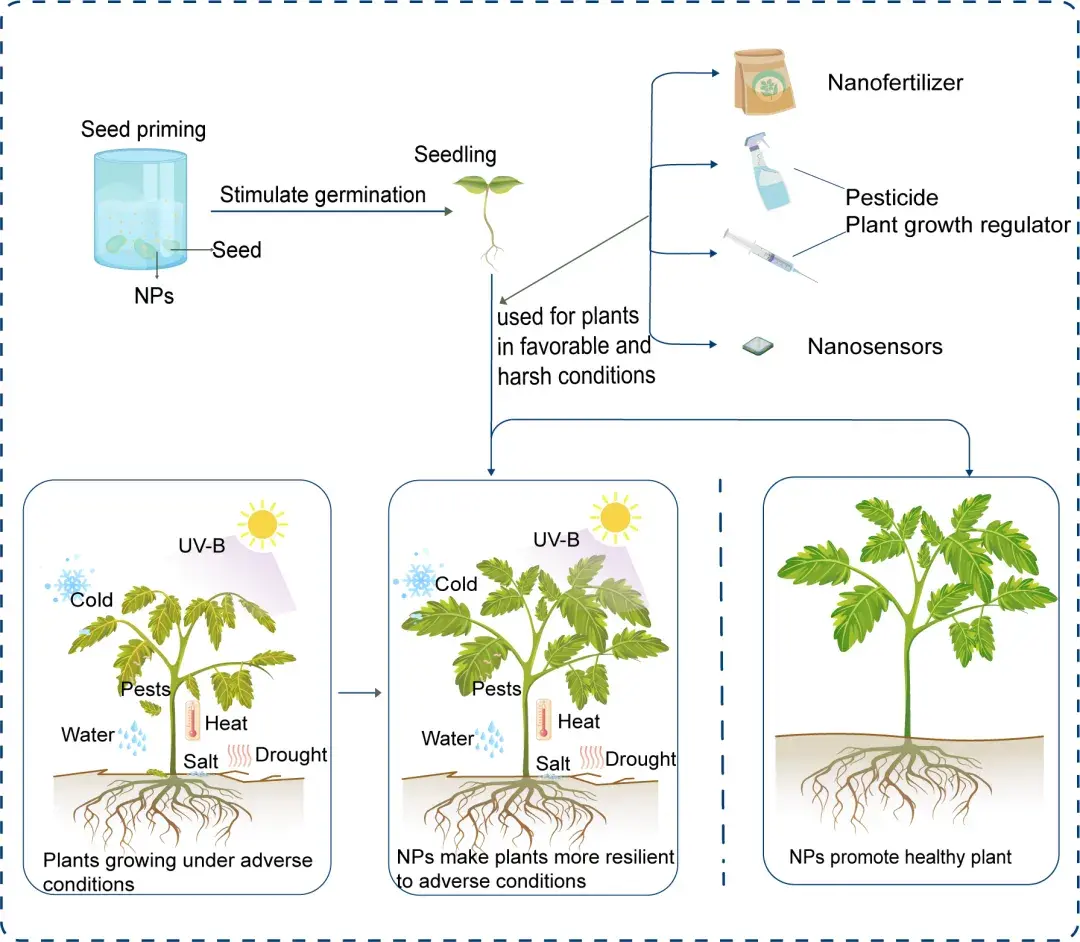
This review explores the mechanisms by which nanoparticles act on plants, the effects on plant abiotic stress responses, the potential of nanotechnology to improve crop yield and quality, and the need for comprehensive examination of the environmental impact and safety of nanomaterials.
Abiotic Stress Responses
TabHLH27 orchestrates root growth and drought tolerance to enhance water use efficiency in wheat
Dongzhi Wang, Xiuxiu Zhang, Yuan Cao, Aamana Batool, Yongxin Xu, Yunzhou Qiao, Yongpeng Li, Hao Wang, Xuelei Lin, Xiaomin Bie, Xiansheng Zhang, Ruilian Jing, Baodi Dong, Yiping Tong, Wan Teng, Xigang Liu, Jun Xiao
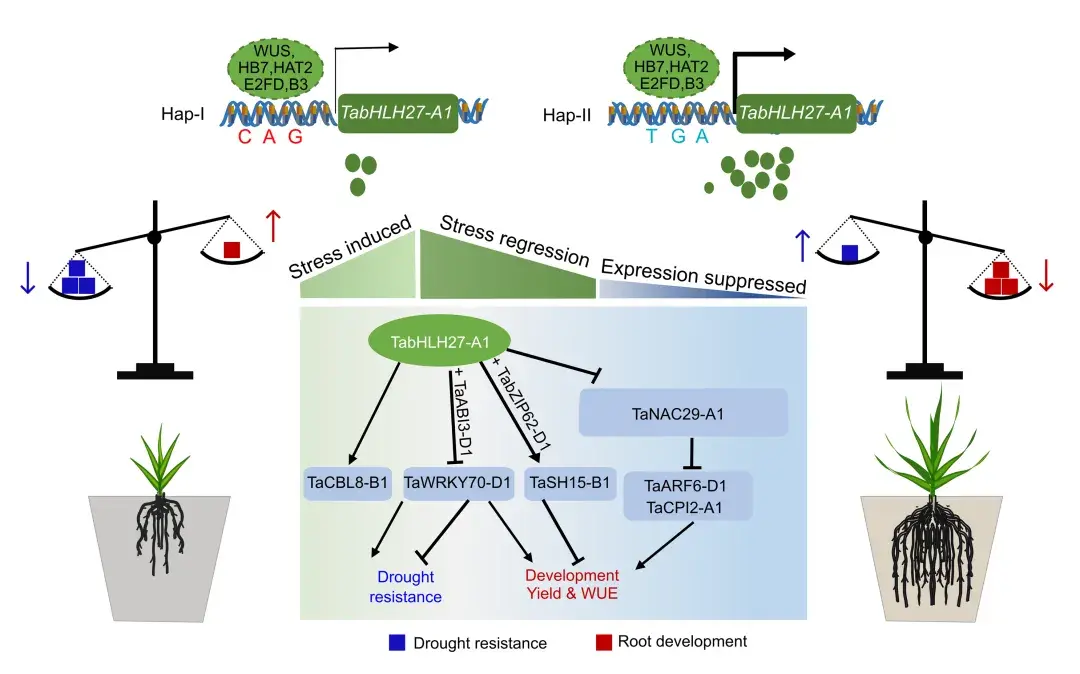
The transcription factor TabHLH27-A1 orchestrates wheat root growth and drought tolerance, with an elite allele ofTabHLH27-A1improving yield under water scarcity, thus providing a breeding target for enhancing water use efficiency in wheat.
Ca²⁺-independent ZmCPK2 is inhibited by Ca²⁺-dependent ZmCPK17 during drought response in maize
Xiaoying Hu, Jinkui Cheng, Minmin Lu, Tingting Fang, Yujuan Zhu, Zhen Li, Xiqing Wang, Yu Wang, Yan Guo, Shuhua Yang, Zhizhong Gong

In maize, phosphorylation of the calcium-dependent protein kinase ZmCPK2 in response to Ca²⁺ oscillations triggered by drought or abscisic acid inhibits its activity, resulting in inactivation of the YABBY family transcription factor ZmYAB15 and inducing drought stress responses.
Phosphorylation of ZmAL14 by ZmSnRK2.2 regulates drought resistance through derepressingZmROP8expression
Yalin Wang, Jinkui Cheng, Yazhen Guo, Zhen Li, Shuhua Yang, Yu Wang, Zhizhong Gong
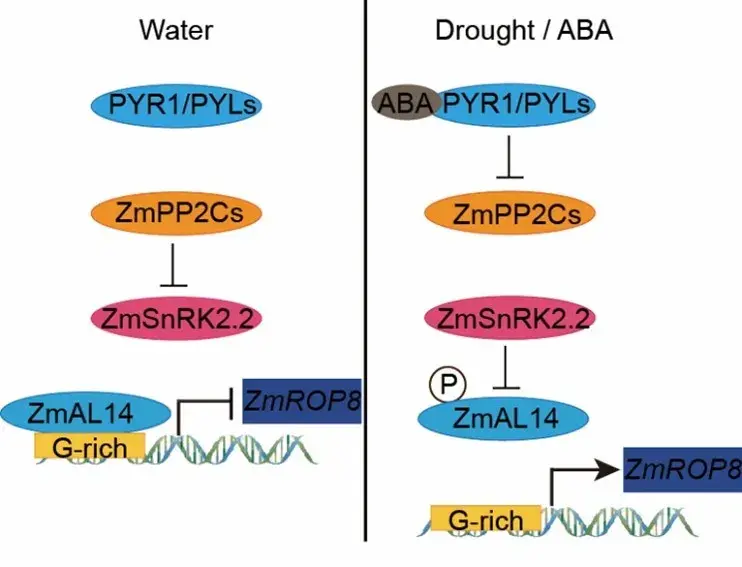
Under drought stress or abscisic acid (ABA) treatment, a kinase cascade regulates the Alfin-like family protein ZmAL14, removing its repression of the dehydration-induced Rho-like small guanosine triphosphatase geneZmROP8, thus activating drought stress responses.
Cell and Developmental Biology
The miR159a-DUO1module regulates pollen development by modulating auxin biosynthesis and starch metabolism in citrus
Yanhui Xu, Wenxiu Tian, Minqiang Yin, Zhenmei Cai, Li Zhang, Deyi Yuan, Hualin Yi, Juxun Wu

Overexpression of the microRNA miR159a and knockout of the MYB transcription factor geneDUO1in citrus led to pollen development defects and abnormal starch metabolism. The miR159a–DUO1module acts on auxin and starch metabolism to regulate pollen development in citrus.
GmNF-YC4 delays soybean flowering and maturation by directly repressingGmFT2aandGmFT5aexpression
Yupeng Cai, Li Chen, Xiaoqian Liu, Weiwei Yao, Wensheng Hou
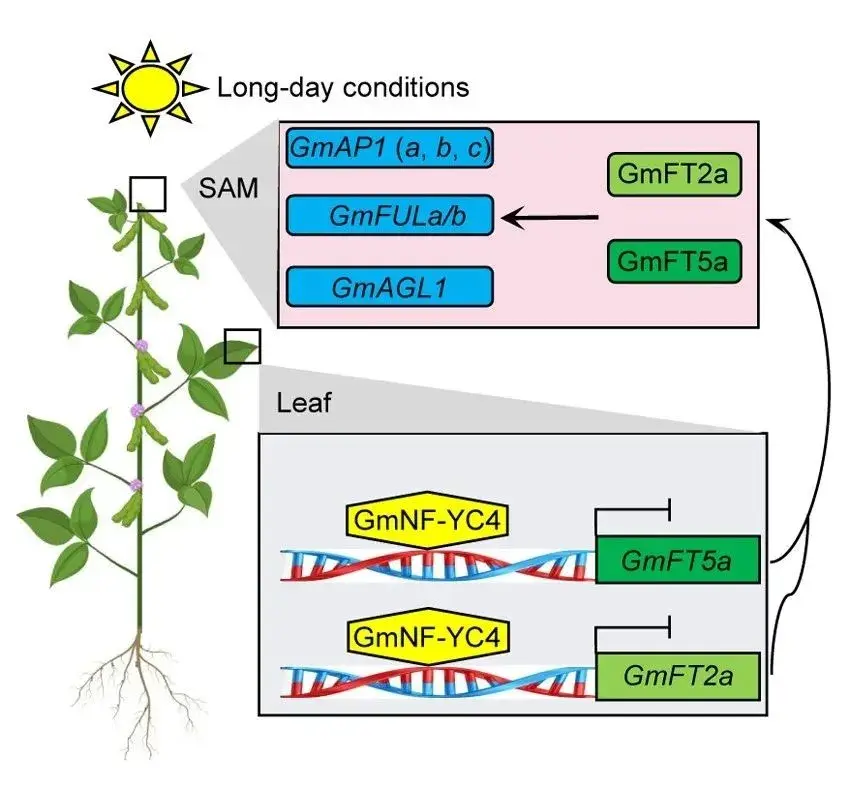
GmNF-YC4 functions as a flowering suppressor in soybean under long-day conditions, directly repressing the expression ofGmFT2aandGmFT5a.GmNF-YC4underwent strong selection during domestication, with oneGmNF-YC4allele predominantly found inGlycine sojaand another predominantly found inGlycine max.
Transcription factor OsWRKY11 induces rice heading at low concentrations but inhibits rice heading at high concentrations
Lirong Zhao, Yunwei Liu, Yi Zhu, Shidie Chen, Yang Du, Luyao Deng, Lei Liu, Xia Li, Wanqin Chen, Zhiyu Xu, Yangyang Xiong, You Ming, Siyu Fang, Ligang Chen, Houping Wang, Diqiu Yu
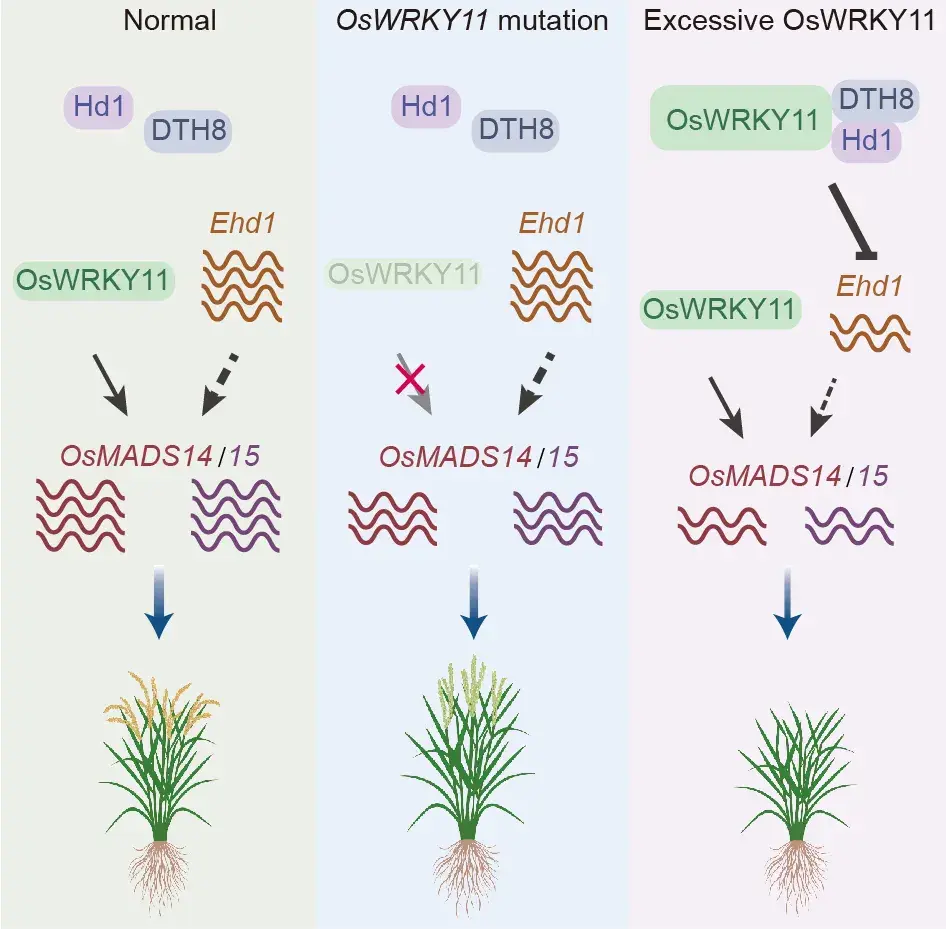
Under normal conditions, low concentrations of OsWRKY11 facilitate flowering by upregulatingOsMADS14/15. However,OsWRKY11overexpression and drought-inducedOsWRKY11upregulation result in OsWRKY11 accumulation, and formation of a complex containing OsWRKY11, Heading date 1, and Days to heading date 8, which inhibitsEarly heading date 1expression, thus delaying flowering.
Molecular Ecology and Evolution
Population genomics highlights structural variations in local adaptation to saline coastal environments in woolly grape
Jutang Jiang, Zeyu Zhang, Yucong Bai, Xiaojing Wang, Yuping Dou, Ruiman Geng, Chongyang Wu, Hangxiao Zhang, Cunfu Lu, Lianfeng Gu, Jian Gao

Population genomics and a haplotype-resolved near telomere-to-telomere reference genome highlight the role of structural variation in local adaptation to saline coastal environments in woolly grape (Vitis retodrii) and identifies candidate genes for future breeding programs for grapevine and its rootstocks.
Molecular Physiology
An orchestrated ethylene–gibberellin signaling cascade contributes to mesocotyl elongation and emergence of rice direct seeding
Yusong Lyu, Xinli Dong, Shipeng Niu, Ruijie Cao, Gaoneng Shao, Zhonghua Sheng, Guiai Jiao, Lihong Xie, Shikai Hu, Shaoqing Tang, Xiangjin Wei, Peisong Hu
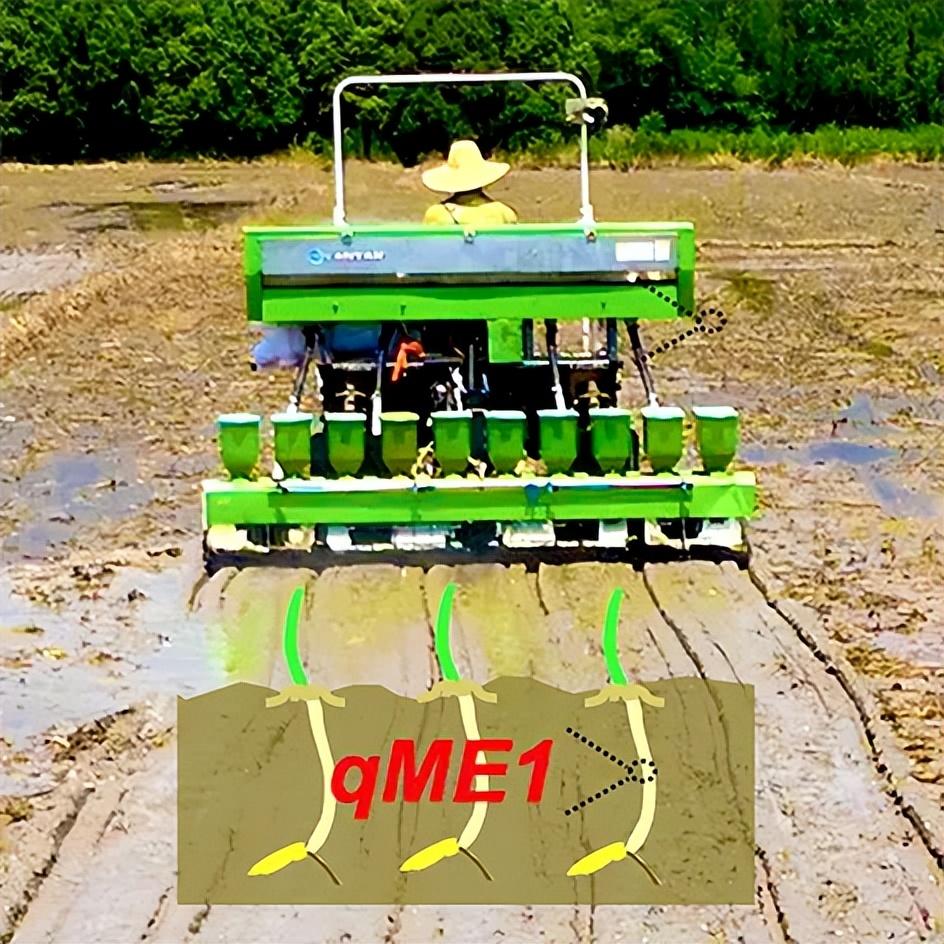

We identified a major quantitative trait locus,mesocotyl elongation1(ME1), which harbors the rice Green Revolution geneSemi-Dwarf1 (SD1), encoding a GA20-oxidase for gibberellin (GA) biosynthesis. An orchestrated ethylene–GA signaling cascade coordinates the ME and emergence of rice seedlings. Furthermore, we found a potential application forME1in modern rice direct-seeding breeding.
Natural variation inMORE GRAINS 1regulates grain number and grain weight in rice
Yingchun Han, Qianfeng Hu, Nuo Gong, Huimin Yan, Najeeb Ullah Khan, Yanxiu Du, Hongzheng Sun, Quanzhi Zhao, Wanxi Peng, Zichao Li, Zhanying Zhang, Junzhou Li
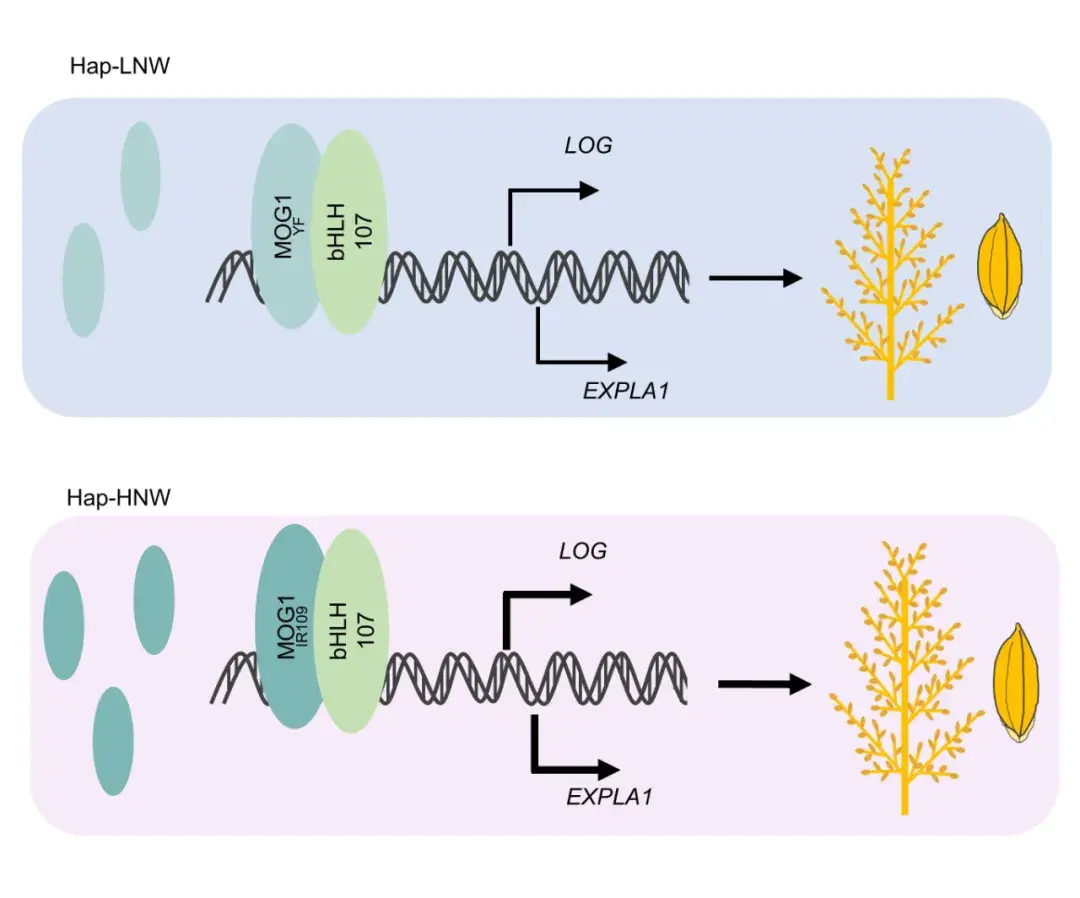
The bHLH transcription factor MORE GRAINS 1 (MOG1) positively regulates grain yield in rice by activating the expression of the cytokinin-activating enzymeLONELY GUYand the cell expansion geneEXPANSIN-LIKE 1. The haplotype Hap-HNW has higherMOG1expression and transcriptional activation activity, resulting in more and heavier grains.
Plant Biotic Interactions
OsATL32 ubiquitinates the reactive oxygen species-producing OsRac5–OsRbohB module to suppress rice immunity
Yuqing Yan, Hui Wang, Yan Bi, Jiajing Wang, Muhammad Noman, Dayong Li, Fengming Song
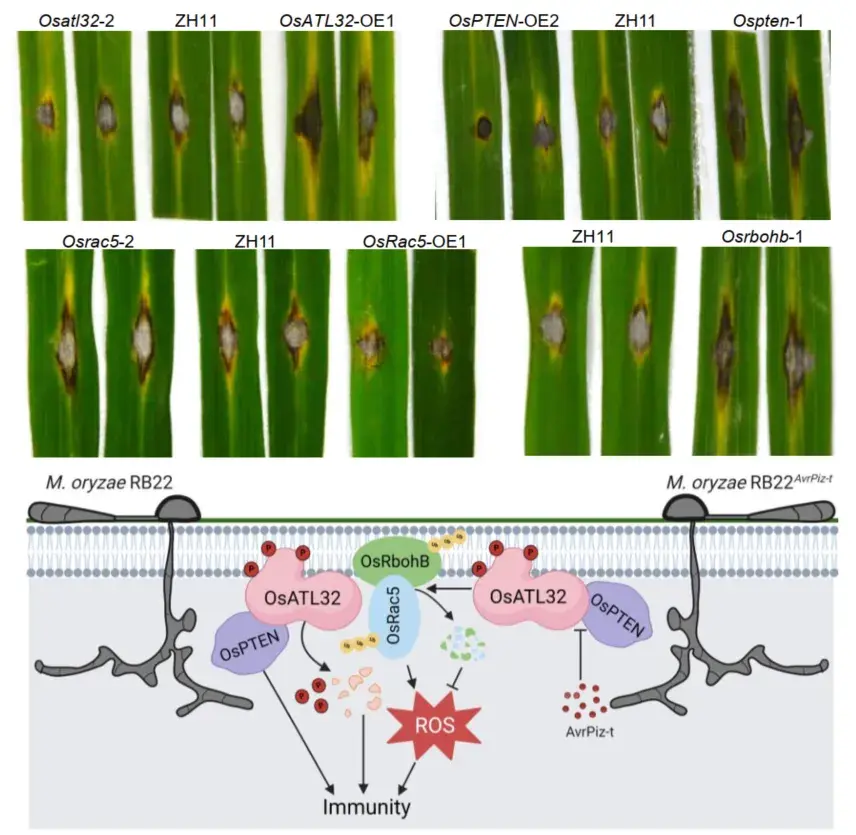
The plasma membrane-localized E3 ubiquitin ligase OsATL32, which is dephosphorylated and destabilized by the protein phosphatase OsPTEN, negatively contributes to rice immunity against blast and bacterial leaf blight diseases by targeting the reactive oxygen species–producing OsRac5–OsRbohB module for degradation.
A vicinal oxygen chelate protein facilitates viral infection by triggering the unfolded protein response inNicotiana benthamiana
Zhihong Guo, Ning Jiang, Menglin Li, Hongfang Guo, Qi Liu, Xinyu Qin, Zongying Zhang, Chenggui Han, Ying Wang
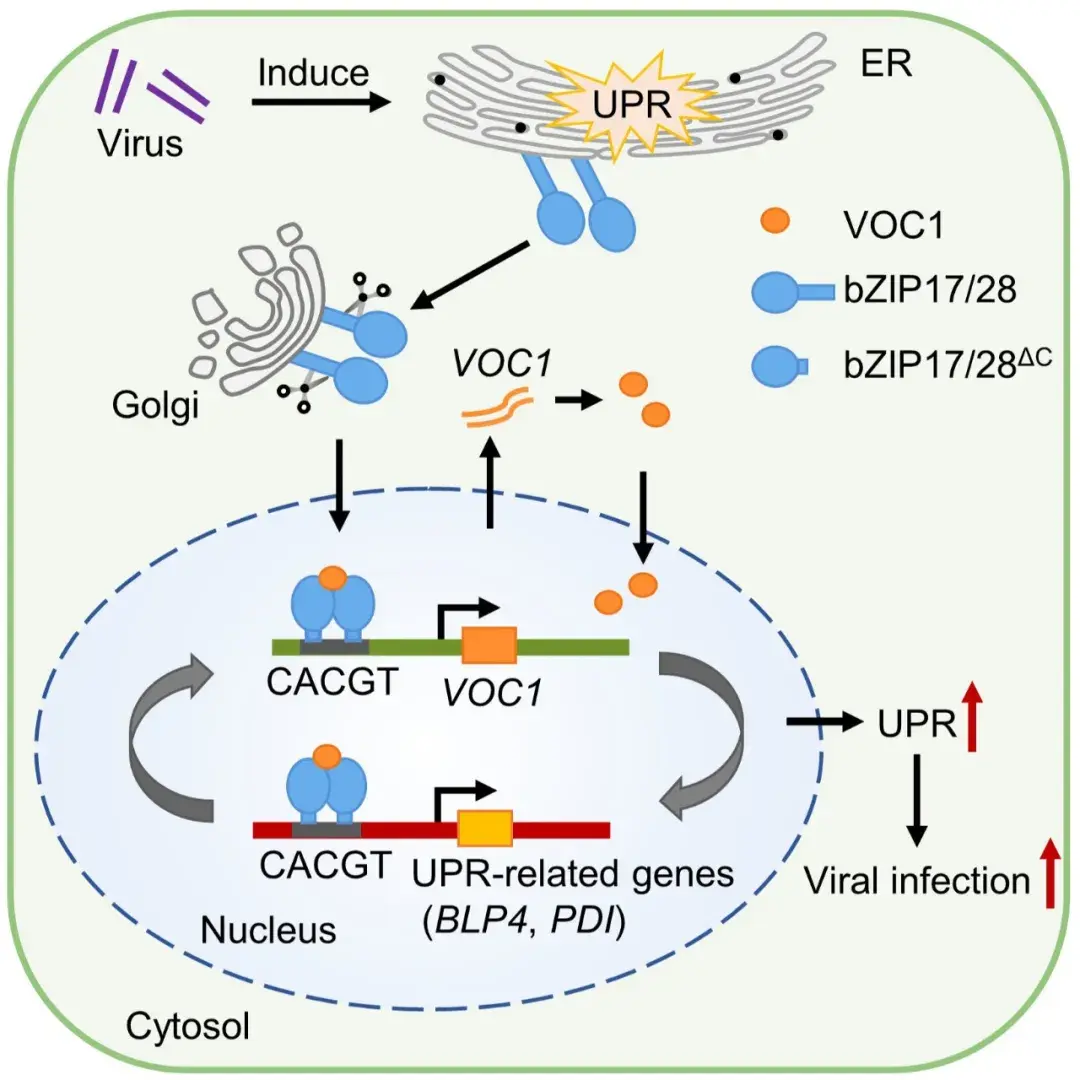
InNicotiana benthamiana, Beet necrotic yellow vein virus infection triggers the bZIP17/28 branch of the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR), which activates transcription of the vicinal oxygen chelate protein geneVOC1. VOC1 enhances bZIP17/28 self-interaction and promoter binding activity in the nucleus, thereby facilitating the bZIP17/28-mediated UPR, which enhances viral infection.
Plant Reproductive Biology
Sporophytic control of tapetal development and pollen fertility by a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in rice
Jianguo Zeng, Manman Duan, Yiqing Wang, Guangtao Li, Yujing You, Jie Shi, Changhao Liu, Jinyang Zhang, Juan Xu, Shuqun Zhang, Jing Zhao
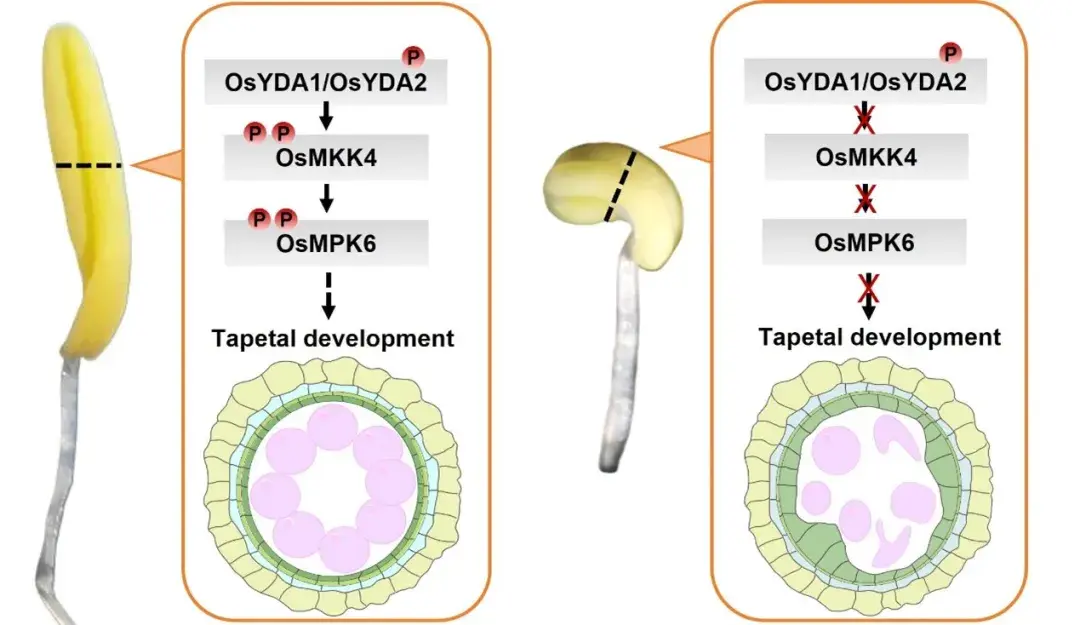
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade composed of OsYDA1/OsYDA2, OsMKK4, and OsMPK6 plays an important role in tapetal development and male gametophyte fertility. Loss of function of this MAPK cascade leads to anther indehiscence, enlarged tapetum, and aborted pollen grains.
AtRKD5 inhibits the parthenogenic potential mediated byAtBBM
Qiyan Liu, Dongfen Han, Denghu Cheng, Jinfan Chen, Shujuan Tian, Jiafa Wang, Man Liu, Li Yuan
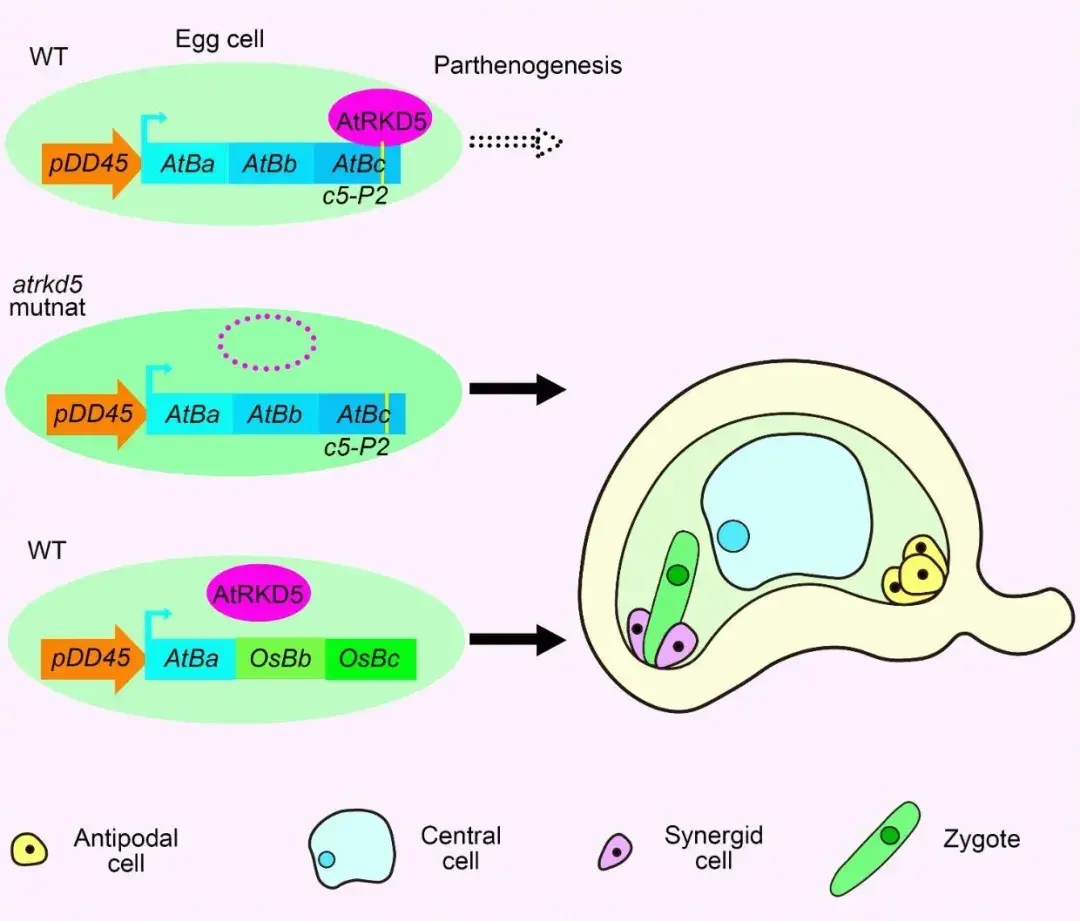
InArabidopsis, the RWP-RK domain-containing transcription factor AtRKD5 directly repressesBABY BOOM (AtBBM)in egg cells, but cannot repress the chimeric geneOsbcAta-BBM, resulting in ectopicAtBBMexpression in the egg cells and initiation of parthenogenesis. Therkd5mutants show a similar phenotype, producing haploid offspring through parthenogenesis.
